
Pacemaker implantation is a medical procedure where a small electronic device is surgically placed under the skin, usually near the chest, to regulate abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) by sending electrical impulses to the heart.
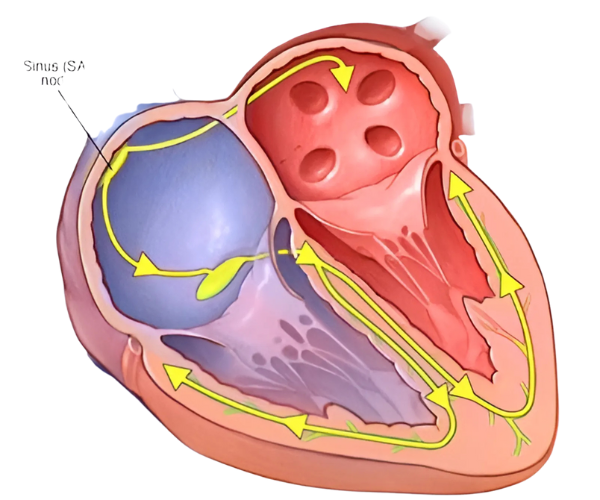
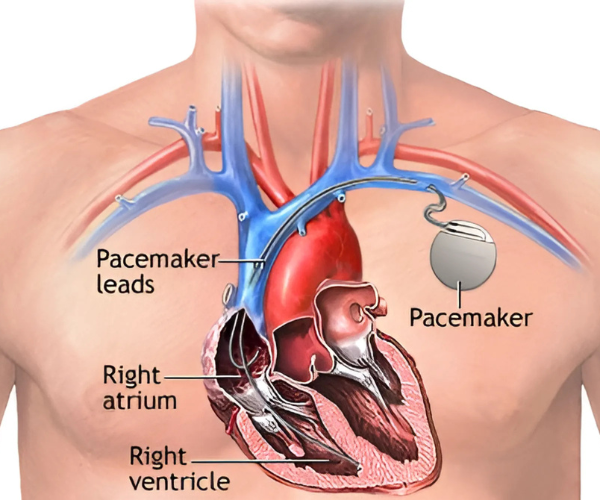
A pacemaker consists of a pulse generator (battery and electronic circuit) and leads (wires) that connect to the heart. It works by:
✔ Monitoring the heart’s rhythm
✔ Detecting irregularities (slow or blocked electrical signals)
✔ Sending electrical impulses to stimulate the heart when needed, ensuring a normal heart rate.
The main purpose of a pacemaker is to:
✔ Maintain a stable heart rate when the heart beats too slowly (bradycardia)
✔ Improve heart function in conditions like heart failure
✔ Prevent symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, and fatigue caused by abnormal heart rhythms

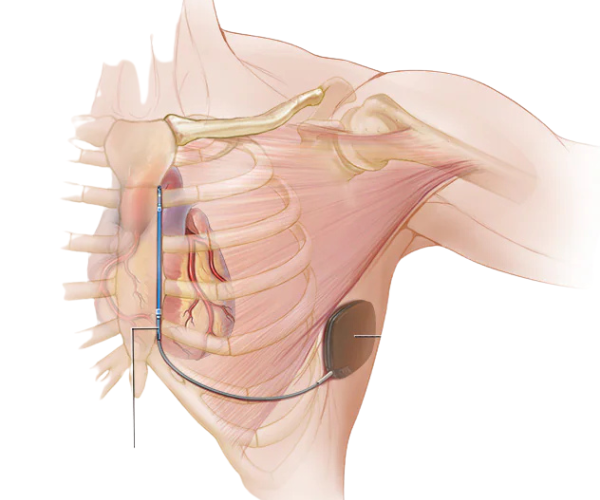
Pacemaker implantation is recommended for individuals with:
✔ Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
✔ Heart block (delayed or blocked electrical signals in the heart)
✔ Atrial fibrillation with slow heart rate
✔ Heart failure with conduction disorders
✔ Syncope (unexplained fainting episodes due to heart rhythm problems)