
Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure used to check for blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. A contrast dye is injected into the arteries, and X-ray imaging (fluoroscopy) is used to detect any abnormalities.

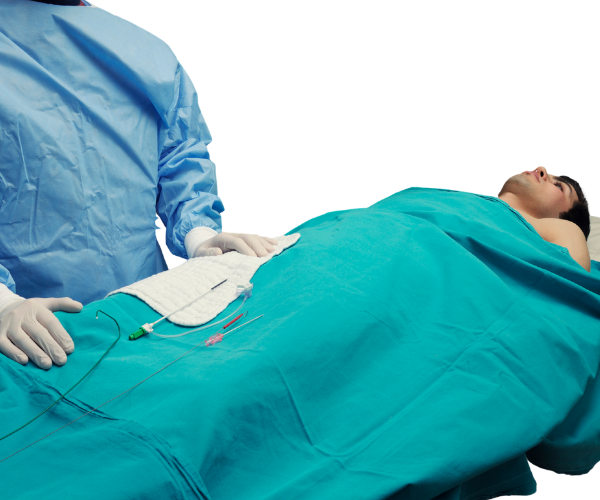
✔ Identifies blockages in coronary arteries
✔ Helps diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD)
✔ Assists in planning further treatment like angioplasty or bypass surgery
✔ Restores blood flow to the heart
✔ Relieves chest pain (angina)
✔ Prevents heart attacks and improves heart function
✔ Minimizes the need for more invasive procedures like bypass surgery
✔ Symptoms of coronary artery disease – chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness
✔ Abnormal stress test results indicating poor blood flow to the heart
✔ Acute heart attack (STEMI/NSTEMI) requiring immediate intervention
✔ Severe artery blockages detected through non-invasive tests
✔ A thin catheter is inserted into a blood vessel (usually from the wrist or groin) and guided to the coronary arteries.
✔ A contrast dye is injected through the catheter to make arteries visible on an X-ray.
✔ X-ray imaging (fluoroscopy) captures real-time images of the heart’s arteries, detecting narrowing, blockages, or abnormalities.
✔ A catheter with a balloon tip is inserted into the blocked artery.
✔ The balloon is inflated, pushing the plaque against the artery walls, restoring blood flow.
✔ A stent (metal mesh tube) is often placed to keep the artery open permanently.