
Device closure is a minimally invasive procedure used to repair congenital heart defects (CHDs) such as Atrial Septal Defect (ASD), Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD), and Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA). It involves placing a specialized closure device inside the heart to seal abnormal openings between heart chambers or vessels.
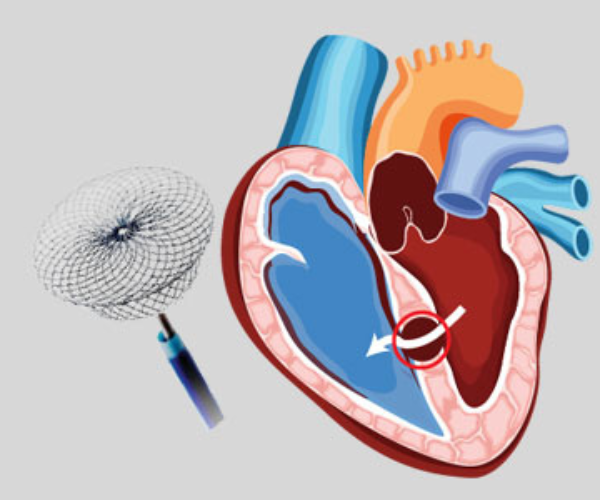
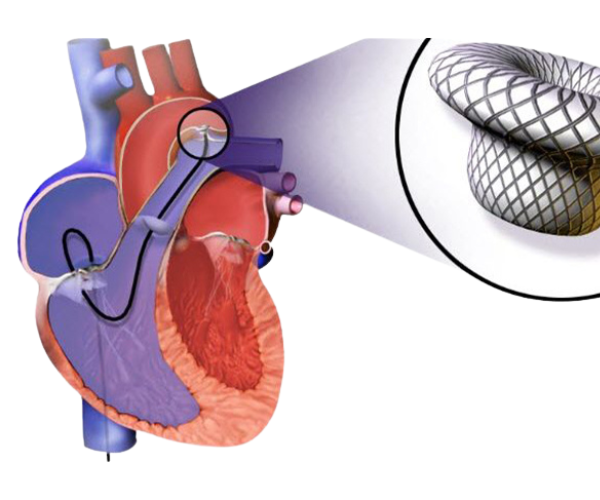
✔ A catheter (thin tube) is inserted through a blood vessel, usually from the groin.
✔ The closure device (made of mesh or metal) is delivered through the catheter to the defect site.
✔ The device expands and securely seals the abnormal opening.
✔ Over time, heart tissue grows over the device, permanently closing the defect.
✔ The catheter is removed, and the procedure is completed without the need for open-heart surgery.
✔ Corrects congenital heart defects without open-heart surgery.
✔ Prevents complications like heart failure, stroke, or lung damage.
✔ Restores normal blood flow between heart chambers.
✔ Reduces symptoms such as fatigue, breathlessness, and irregular heartbeats.
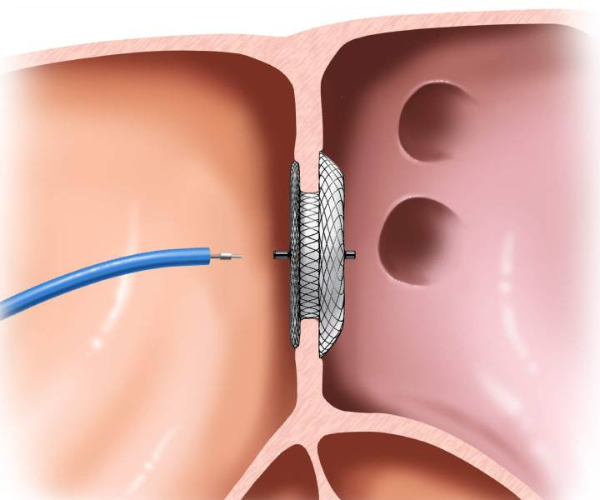
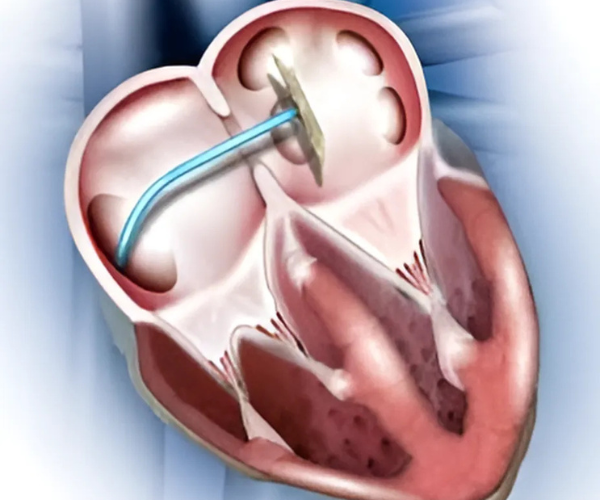
✔ Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) – A hole between the heart’s upper chambers.
✔ Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) – A hole between the heart’s lower chambers.
✔ Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) – An abnormal connection between the aorta and pulmonary artery.
✔ Patients with small to moderate defects that can be closed without surgery.